In semiconductor testing, load boards are always being performed production stability and test reliability, providing exact electrical connections between the tester and IC for signal transfer and response measurement. The features of low signal degradation and low crosstalk help validate high-speed, high-frequency components, and load boards must meet test requirements. Thus, they prevent expensive field failures in complicated semiconductor devices while spotting prospective issues early. This article will give an overview of load boards, their types, uses, and benefits.
What is a Load Board?
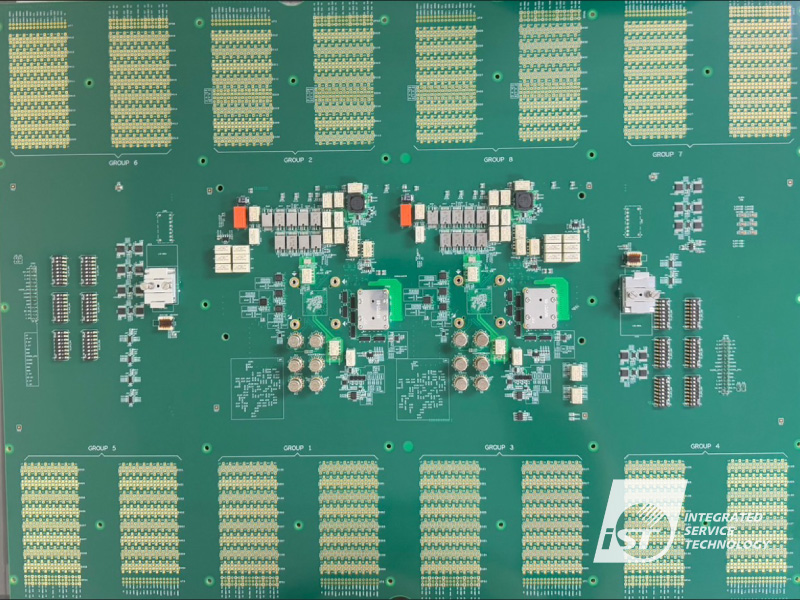
Interfacing the device under test (DUT) and automatic test equipment (ATE) in semiconductor testing requires load boards. Their accurate mapping of DUT I/O pins to ATE channels preserves signal integrity and avoids parasitics. To obtain the DUT’s true performance metrics, load boards must handle milliohm impedance matching and nanosecond timing accuracy when testing high-frequency RF integrated circuits.
Testing BGA, QFN, and LGA assembled IC packages is easy using load boards. With Kelvin probing for low-voltage measurements and high-current pathways, they deliver precise signals. E.g., the load board must maintain signal channels with low interference and accurate impedance management while testing a BGA package at GHz frequencies.
Key Components of a Load Board
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board): The PCB is the key link between the DUT and the test equipment. It provides the routing and signal integrity for accurate testing. The PCB provides minimal signal degradation with controlled impedance traces and multilayered designs. Moreover, it may include embedded decoupling capacitors near the DUT to moderate noise and stabilize power delivery.
- Sockets and Connectors: Sockets and connectors are the physical interfaces on the load board that connect the DUT to the test equipment. The types of contact pins must be concerned for precision-engineered contact resistance, accommodate high pin counts and fine pitch without compromising electrical performance.
- Components: Apply for resistors and capacitors on the signal pathways and control impedance for signal fidelity on the load board. On the other hand, SI(Signal integrity) and PI(Power integrity) simulation will ensure clean signals transmitted to DUT and minimize effects through thoughtful electronics design.
Types of Load Boards
High-Frequency Load Boards
High-frequency load boards evaluate RF and microwave equipment at 30-50 GHz ranges. They need design to cut signal loss and impedance mismatches that skew readings. E.g., testing 5G parts requires boards with ultra-low-loss materials.
Mixed-Signal Load Boards
Mixed-signal load boards test ADCs and DACs that handle analog and digital signals. They must provide low-jitter digital signal integrity and broad analog bandwidth (several hundred MHz). Such boards may include LVDS or SPI digital interfaces and impedance-matched analog test points. For example, to limit IC degradation while testing a 16-bit ADC with a 200 MHz input, the board might preserve less than 0.5 dB signal attenuation and little congestion between digital and analog sections.
Interface Boards
PIB(Probe Interface Board) for Teradyne and WPI(Wafer Probe Interface) for Advantest connect the pogo pins of test head to the pogo pin of pogo tower, maps the rectangular layout of test head to circular layout of pogo tower. Customer sometimes may require a interface board on specified test slots connecting with nonstandard resource.
Applicable Field of Load Boards
Final Test
Load boards are key in the final test phase of IC manufacturing. Their signal integrity and power supply are fundamental for IC performance evaluation. In high-frequency RF IC testing, load boards must match impedance to lower signal reflection and provide accurate measurements. Load boards have large pin counts—around 1000-5000 I/O pins—and require careful layout to manage signal routing and avoid distortion.
Platform
- Advantest: EXA, V93K, T2000, ND1~4
- Teradyne: Ultraflex+, Ultraflex, J750, ETS
- Cohu: Diamondx, D10, ASL
- NI: STS
- Chroma: 3360, 3350, 3380, 3680
- KYEC: E320, I6000, I2K
- YTEC: S50, S100, S300
Advantages of Using Load Boards
- Improved Accuracy: Quality load boards boost semiconductor testing precision.
- Increased Efficiency: Load boards speed up and lower the cost of IC testing.
- Enhanced Reliability: IC load boards avert field failures and keep performance.
- Scalability: Scaling load boards for many devices and tests gives them versatility.