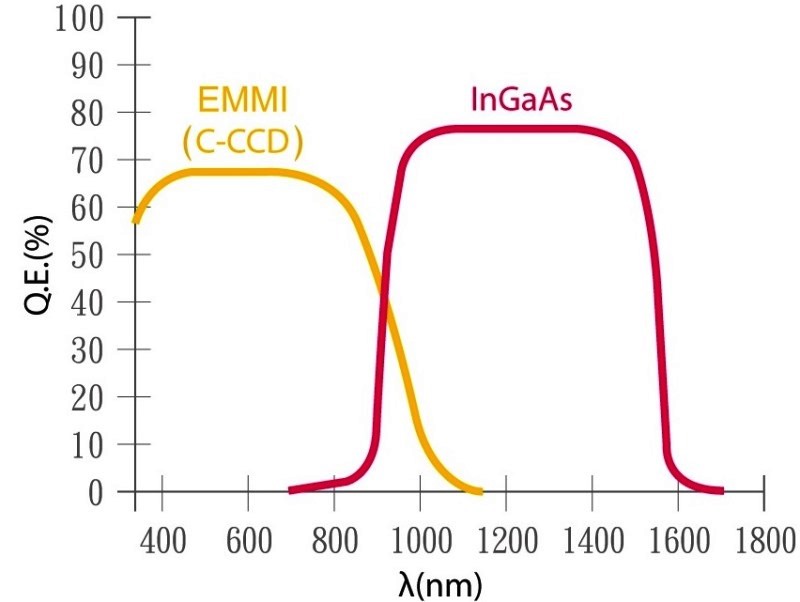
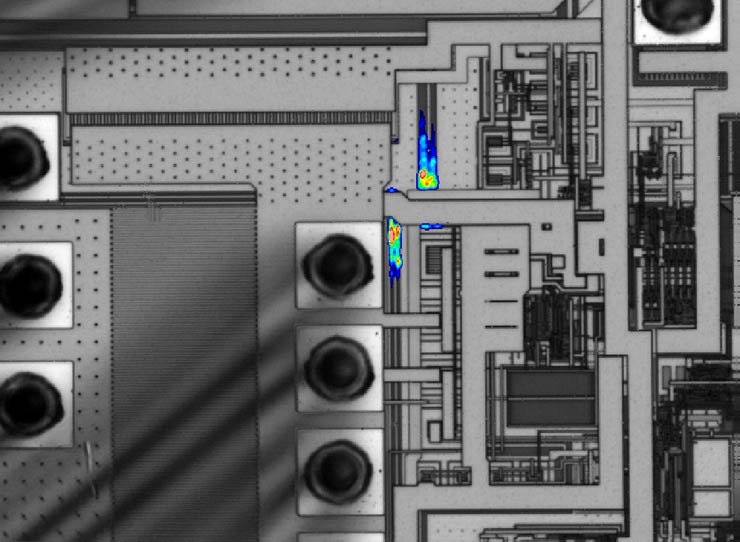
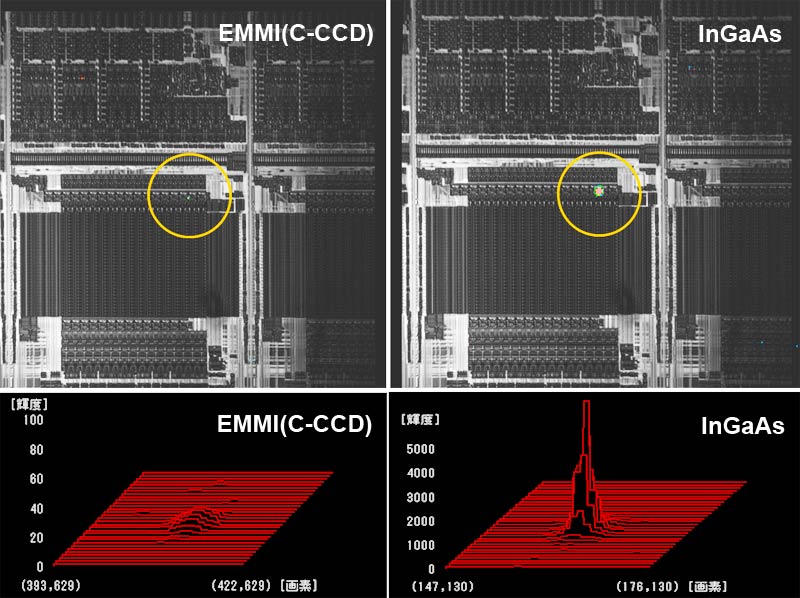
The InGaAs EMMI and EMMI have the same principle and function the same way. Both detect photons are triggered by electron-electron hole reunion and hot carriers. They differ in that InGaAs has better sensitivity and may detect longer wave length range 900-1700nm (versus 350-1100nm of EMMI) which is the same wave length spectrum of IR.
The Superiority of iST
iST equipped with double side Probe station to reduce the time and cost for sample preparation.
Case Sharing
InGaAs and EMMI have similar applications but InGaAs features more advantages as follows
- Detects defects in a shorter period, 5 to 10 times shorter than EMMI.
- Detects defects that EMMI is unable to detect (also detects micro current leakage and defects of advanced processes).
- It’s capable of detecting micro Metal Bridges.
- IR lights benefits better penetration rate over silicon substrate for IC backside positioning analysis
Conditions where hot spots are detected
- Defects that cause hot spots
- Junction Leakage
- Contact spiking
- Hot electrons
- Latch-Up
- Gate oxide defects / Leakage(F-N current)
- Poly-silicon filaments
- Substrate damage
- Mechanical damage
- Junction Avalanche
- Hot spots that existed originally
- Saturated/ Active bipolar transistors
- Saturated MOS/ Dynamic CMOS
- Forward biased diodes /Reverse biased diodes(breakdown)
Conditions where hot spots cannot be detected:
- Defects without light spots
- Ohmic short and Metal short
- Hot spots being blocked
- Buried Junctions
- Buried Junctions and Leakage sites under metals.
Limited by lens rotation angles, a maximum of 4 probe manipulators (4 probe tips) can be installed on the stage. Maximum height of sample: 10 cm. Requires totally-dark-chamber operation without the existence of light emitting devices.
Contact Window | Ms. Liu/Sylvia | Tel:+886-3-5799909#6780 | Email:web_EFA@istgroup.com