Issued Date:2019/11/12Die Bonding
Issued By:iST
Die bonding is one of the key steps in the semiconductor’s packaging process.
Replacing manual operation with automatic equipment is inevitable as die bonding standards get more demanding.
Die Bonding
The IC die bonding process is one of the key steps in the semiconductor’s packaging process and its quality is critical to the capacity of the entire packaging process. Several different bonding processes have been developed addressing the evolution of semiconductors and performance of increasing frequency signals required by communication products.
IC packaging has been focused on wire bonding and being supported by die bonding which are manual operations centered in most cases. With terminal devices becoming increasingly compact and the looming 5G era, the die bonding processes, featuring different electric performance among individual processes, are challenged by more and more stringent standards.
iST, the leader in the semiconductor verification and analysis industry, is helping its customers run these verification test and lab analysis operations easily and effectively by providing fast IC packaging services for the manufacturer of experimental engineering samples. Addressing the stringent standards over die bonding in the 5G era, the iST fast packaging lab is launching the die bonding equipment to execute operation items and render a quality of bonding which no manual operation can rival.
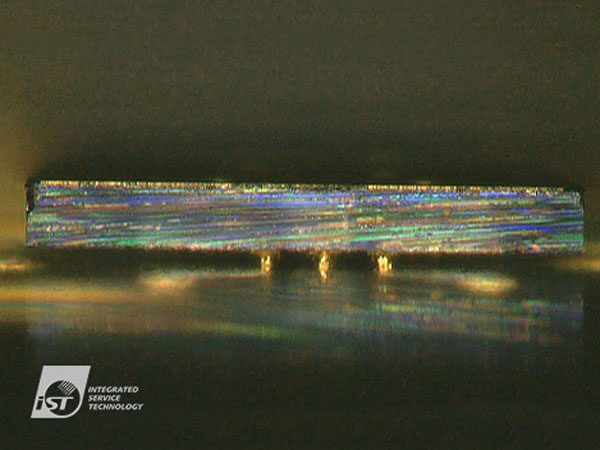
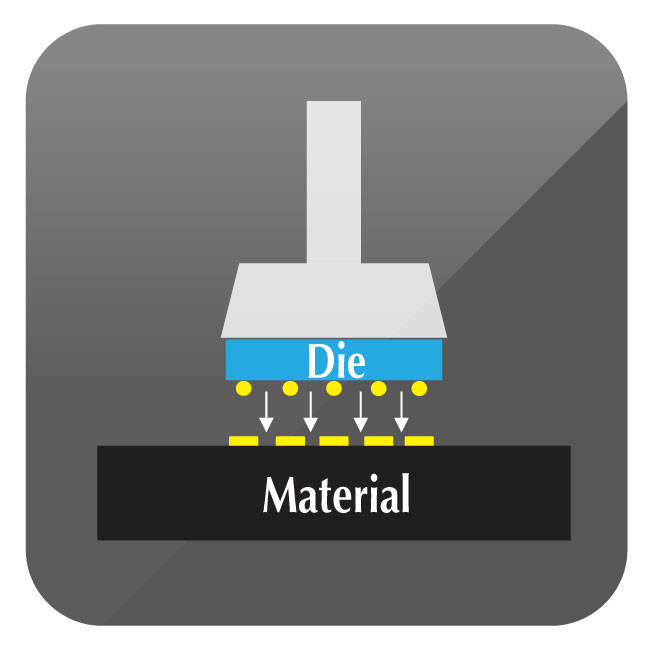
The automatic bonding process comes in three steps, Die Sorting, Adhesive Die Bonding, and Eutectic Process as illustrated below:
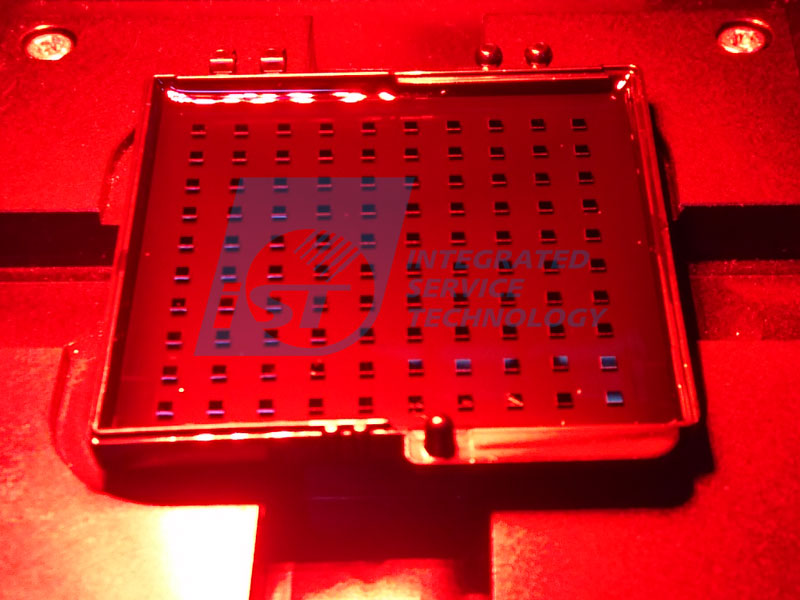
Die Sorting
Adhesive Die Bonding
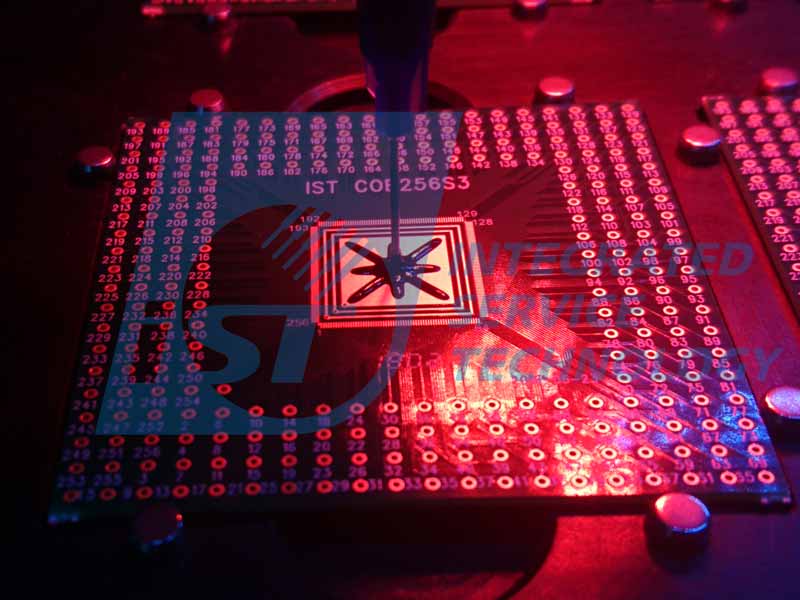
Bond dies to substrate or material with adhesives which may be conductive or non-conductive. Get the adhesives out of a low-temp freezer and warm it in an environment of normal temperature into liquid before adding them, usually in an amount aligned with the size of dies measured in advance, on substrate or material with a manual spotter. The trays are then placed into an oven to bake dry and solidify the adhesives.
The iST die bonding device is equipped with a micro screw valve driven spotting valve to apply a more accurate die bonding adhesives amount than its pneumatic rivals and controls die positioning in a range of ±5μm @ 3 Sigma as required by customers.
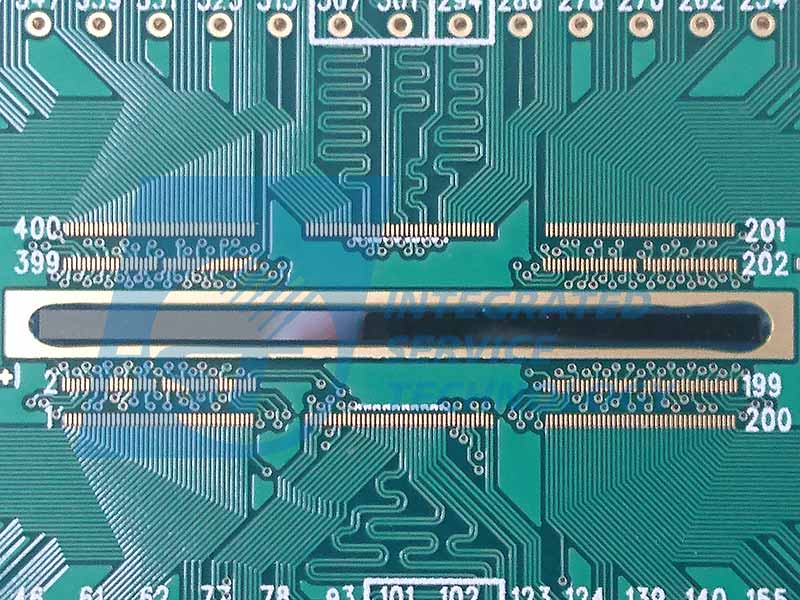
Eutectic Process
Bond two metal pieces of the same or different phases to give the intermetallic bonded one with electric conduction by the following two processes:
(1)Thermocompression die bonding
The thermocompression die bonding process heats the solder layer into liquid while keeping another soldering spot at a temperature just below the solder melting point to enable the liquified solder to flow to the other bonding surface and shape up an intermetallic bond, AKA wetting. You may apply pressure atop the bonding points to prevent liquidified solder from shifting the objectsand apply flux to get the best intermetallic bonding. Gold-tin solders are used in most thermocompression die bonding processes now.
- Process Application
– Copper pillar or solder ball Flip chip Bonding
– Gold-Tin devices die bonding
– Gold-Tin AuSn lid seal
– DAF (Die attach film) die bonding
(2)Thermosonic die bonding
The thermosonic die bonding process employs a low-temp, clean, and dry packaging for die bonding. It bonds two metal pieces, gold-gold in most cases, with mechanical supersonic vibration at a temperature below 150℃ rather than over 270℃ temperature required by the rivaling thermocompression. This not only ends up with less damage to sensitive ICs caused by high temperature, but also eliminates the needs of flux and post-soldering cleaning.
- Process Application
– Stud bump flip chip bonding
– Low temp. eutectic die bond
– Optics
(3)Thermocompression die bonding V.S. Thermosonic die bonding:
Process Advantages Disadvantages Thermocompression - Fewer process parameter conditions and less time for trial run
- Higher production efficiency
- Contamination by flux
- High temperature resistance required by the material and relevant components
- Oxidation at high temperature
Thermosonic - Lower process temperature
- More flexibile packaging process
- Lower chip costs
- Less contamination and better cleanliness
- Short ball distance acceptable
- More process parameter conditions and requires more time for trial run
- Supersonic vibration tends to damage MEMS and other sensitive components of chips
The die bonder employed by the iST fast packaging lab comes with two eutectic process options: thermocompression and thermosonic bonding. The former features a heating system for temperatures up to 400 ℃ which can not only set up a temperature rising curve but also heat from the top, bottom, or both top and bottom as well as a downward pressure mechanism with the maximum force output at 3Kg and tolerance at ±5%; the latter comes with a maximum supersonic output power of 100W.
- Process Application
To learn more about our services, just ring Benson Yang at +886-3-579-9909 EXT 6862 or email us at ist_assy@istgroup.com.