Issued Date: 2024/5/10
Issued By: iST
Hsinchu, Taiwan, R.O.C. May 10, 2024 – iST (TWSE:3289), the Automotive Electronics Council (AEC) announced the release of the AEC-Q007 specification in March this year, marking a significant advancement for automotive electronic design and verification. AEC-Q007 focuses on Board Level Reliability (BLR) testing for automotive applications, integrating the design of components with printed circuit boards (PCBs) to provide comprehensive reliability assurance for automotive electronics.
Despite the gradual slowdown in the growth rate of the electric vehicle market compared to previous years, the International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts that by 2035, electric vehicle adoption rates in Europe and North America will exceed 85% and 70%, respectively. In the medium to long term, as countries continue to introduce stricter environmental regulations, the electric vehicle market is expected to continue expanding.
The family members of the AEC Component Technical Committee are AEC-Q100 (IC Chips), AEC-Q101 (Discrete Components), AEC-Q102 (Discrete Optoelectronic Components), AEC-Q103 (MEMS, Microelectromechanical Systems), AEC-Q104 (MCM, Multi-Chip Modules), and AEC-Q200 (Passive Components). These specifications primarily focus on conducting various tests at the component level. Although the AEC-Q104 specification mentions Board Level Reliability (BLR) in Test Group H, it only provides some reference specifications. It wasn’t until March 2024 with the release of AEC-Q007 that the integration of components and printed circuit boards (PCBs) was truly addressed. It elaborates on PCB and Daisy Chain designs, with Daisy Chain design (Figure 1) being the BLR board-level reliability test commonly heard in the industry.
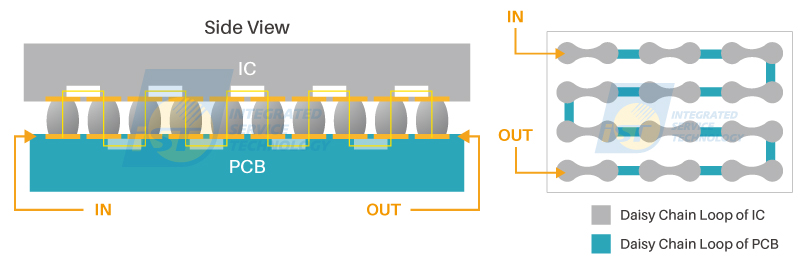 Figure 1: Overview of BLR Daisy Chain Design. (Source: iST)
Figure 1: Overview of BLR Daisy Chain Design. (Source: iST)
As a member of the AEC, iST promptly analyzed the content of the AEC-Q007 specification. The Senior Manager of Reliability Engineering of iST, Mr. Daniel Chuang, stated, the principle of BLR verification involves designing the solder joints and PCB in a conductive mode to create a loop to observe the lifespan of solder joints. During the testing process, measurement equipment is used to obtain real-time information for determining solder joint yield. In AEC-Q007, Daisy Chain design is divided into four levels, with Level 3 being the simplest and Level 0 being the most complex in terms of design difficulty. The AEC-Q007 also provides helpful guidelines, allowing designers to tailor their Daisy Chain design according to their specific requirements.
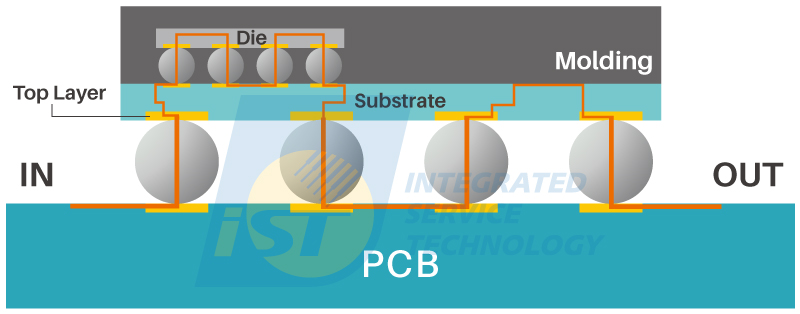 Figure 2: Diagram illustrating the most complex Level 0 Daisy Chain design in the AEC-Q007 specification. (Source: iST)
Figure 2: Diagram illustrating the most complex Level 0 Daisy Chain design in the AEC-Q007 specification. (Source: iST)
Furthermore, AEC-Q007 emphasizes the importance of PCB design in BLR durability. The number of layers and thickness of a PCB does indeed impact the test results. Therefore, when designing a PCB, it is recommended to consider its compatibility with the components. AEC also considers the diversity of environments in which components are ultimately used, making it difficult to have fixed specifications for PCB layer count and thickness. Therefore, AEC does not impose mandatory requirements, but provides a set of PCB design guidelines for reference. The recommended option is an 8-layer PCB with a thickness of 1.6mm.
The Senior Manager of Reliability Engineering of iST, Mr. Daniel Chuang, also stated, although AEC-Q007 is a specification for board-level reliability (BLR), its testing purpose and conditions are somewhat different from the BLR verifications we usually perform. In general, BLR testing, the standard is typically set at 500 or 1000 cycles, and passing these cycles means the product is “verified.” However, unlike traditional BLR testing, AEC-Q007 testing does not aim to determine a pass or fail outcome. Instead, its focus is on understanding the characteristics of the components. It collects failure data of products after mounting components on the board under thermal cycling conditions, serving as a reference for future users or designers.
Since temperature is one of the most challenging conditions for automotive components. As a pioneer standard for automotive BLR, AEC-Q007 takes the lead in proposing the “temperature cycling testing” as the verification method for automotive BLR. iST anticipates that AEC-Q007 will further expand its range of verification items in the future, such as mechanical shock, vibration, humidity testing, etc., to establish a more comprehensive verification process.
About Integrated Service Technology
Founded in 1994, iST began its business from IC circuit debugging and modification and gradually expanded its scope of operations, including Failure Analysis, Reliability Assurance, Material Analysis and so on. iST has offered full-scope verification and analysis services to the IC engineering industry, its customers cover the whole spectrum of the electronics industry from IC design to end products.
In response to the growing future trends, iST has established platforms for 5G/HPC/AI, Automotive Electronics verification, Space Satellite verification, Advanced Processes and Wide-bandgap Semiconductors, LTS ( low-temperature soldering) Process verification platforms, as well as High-speed Transmission Signal Testing, offering comprehensive verification and analysis services. With a commitment to providing complete solutions to customers, iST has expanded its services beyond verification to encompass Wafer Backend Process for mass production service.
http://www.istgroup.com
Press Contact
Deputy Spokes Person
Yuting Chiu
+886-3-579-9909 Ext.1068
Marketing_tw@istgroup.com
